Member stability is a very important issue in the codes and it is very important that we are able to verify and validate the code methods. A small litteratuer study has been performed into the stability analysis of columns and the background documents in Eurocode EN1993-1. This has lead to a paper in which many of the important topics have been investigated. Conserning latteral torsional buckling and interactional member stability analysis a number of student projects have also been performed in collaboration with other international researchers and papers are soon ready for submital. Furthermore investigations into the stability phenomenons of slotted beams and their connections have also been performed.
Slotted Cold-formed Steel Members and Joints
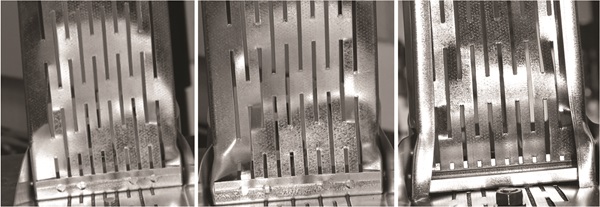
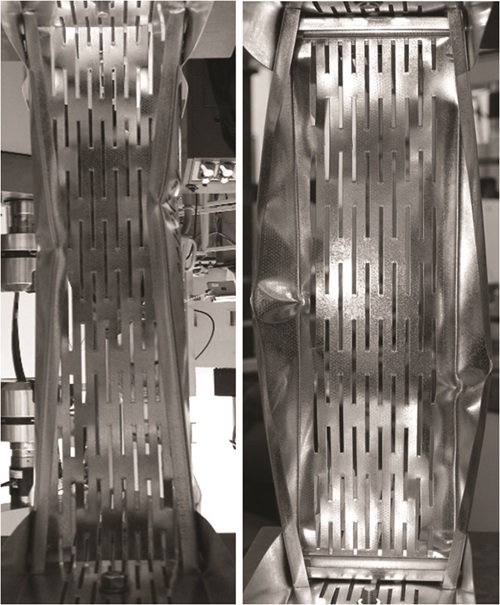
Thin-walled steel structures are widely used due to the high strength and effective use of the materials. Walls made of light gauge steel members in interaction with plaster boards have become a competitive alternative to traditional constructions. To reduce the thermal bridges and in this context optimize the thin-walled framing, slotted light gauge steel members are often used. Several fabricators of lightweight constructions in Scandinavia now have slotted studs in their range, intended for load-bearing external walls.
The importance of the slotted members and joints is related to building components as exterior walls, interior walls and light weight floor structures. This especially includes thermal properties, sound insulation, springiness and vibrations, fire proof as well as building services, architecture, planning and production.
The growing worldwide use and development of light weight steel framing systems including slotted profiles implies a need for further investigation. This also includes the necessity to a better understanding of the system so the design can be improved and lead to an easier, more efficient and correct design.
Future trends
Future trends within the present topic are the use of light steel framing in new applications. The applications are residential housing with in-situ and pre cast concrete structures, office buildings, schools and hotels.
Several municipalities have chosen steel instead of both concrete and timber as structural material because of very negative experiences of allergic and asthmatic problems among students and teachers. The allergic reactions are caused by mold and rot.
There is a big potential of further prefabrication of structural elements to hotels. The repetition of standard elements is big. Room modules or parts of rooms can be prefabricated for export as well as domestic use. There are also great possibilities to use light steel framing in casual building. However, to handle these challenges there is still a need for further investigations and a better understanding of the light steel framing system.
Objectives
Slotted cold-formed steel structures are not yet fully understood, leading to larger and more expensive structures. The slots in the web considerably change the transverse bending and shear stiffness of the web. This has influence on the local and distortional buckling behaviour of the stud and thus also on the behaviour of the joints. By investigating the behaviour and load bearing capacity by means of computational mechanics, experiments and in accordance with existing procedures used in pratice, an optimization of the structures is expected, leading to a much more efficient and improved design.
The objectives of this research are thus to investigate slotted cold-formed steel studs and joints used for external bearing walls in order to observe the behavior of the studs and joints. We are simply looking for the best way or design to transfer load within the structures. This also includes the understanding of the relative contribution of each wall components to the load bearing of the structure, so that through appropriate design, this contribution can be optimized, using the full resistance of each material.
The research within this field is important for the industry to better understand the various behaviors of the steel components when size structures are rapidly increasing and to be able to follow the demands from consulting engineeres and architects when larger and more slender structures are needed by design. The research will definitely benefit the industry by leading to a more efficient and improved design intended to be included in present norms and standards. Further it will optimize the correlation between numerical simulations and physical models.